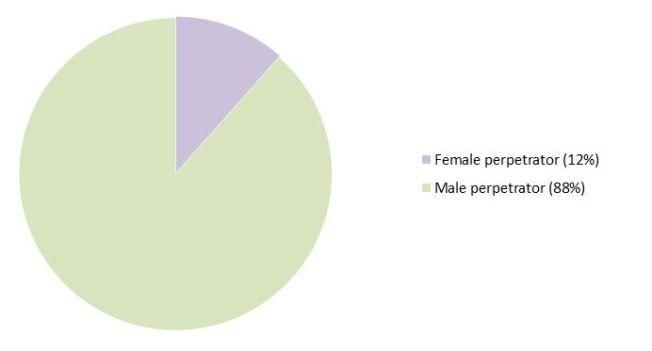
*intimate partner homicides
What could we do if we wanted to hide the reality of men’s violence against women?
Firstly, we might have a ‘gender neutral’ definition of domestic violence. Maybe like the UK government which uses the following definition:
“any incident or pattern of incidents of controlling, coercive, threatening behaviour, violence or abuse between those aged 16 or over who are, or have been, intimate partners or family members regardless of gender or sexuality. The abuse can encompass, but is not limited to: psychological, physical, sexual, financial [and] emotional.”
Not only treating ‘sex’ and ‘gender’ as the same thing, this definition erases sex differences. It includes the phrase ‘regardless of gender’ when in reality men – as a biological sex-class – are overwhelmingly the perpetrators, and women – as a biological sex-class – are overwhelming the victims of ‘domestic violence’ (more on the differences between male and female victims of intimate partner violence here). It is also broad, including violence and abuse committed between any family members. Whilst this can be useful, for example allowing service provision to be made available for those experiencing violence and abuse from any family member, sometimes it is important to focus on ‘intimate-partner violence’, including that committed by former intimate partners.
Secondly, we might present official data in a way that hides the extent of differences between women killed by men and men killed by women
The Office of National Statistics (ONS) definition of partner/ex-partner homicide includes killings by a “spouse, cohabiting partner, boyfriend/girlfriend, ex-spouse/ex-cohabiting partner/ex-boyfriend/girlfriend and adulterous relationship” but also “lover’s spouse and emotional rival”. Data from the ONS found that in 2013/14, consistent with previous years, women were far more likely than men to be killed by partners or ex-partners than men. 84 women, around 53% of female homicide victims (over 16) had been killed by their current or a former partner, compared to 23 men (7% of male victims over 16). So, we could say that government data tells us that one-in-five of those killed though ‘partner violence’ is male. Except this creates a false picture of what is really happening.
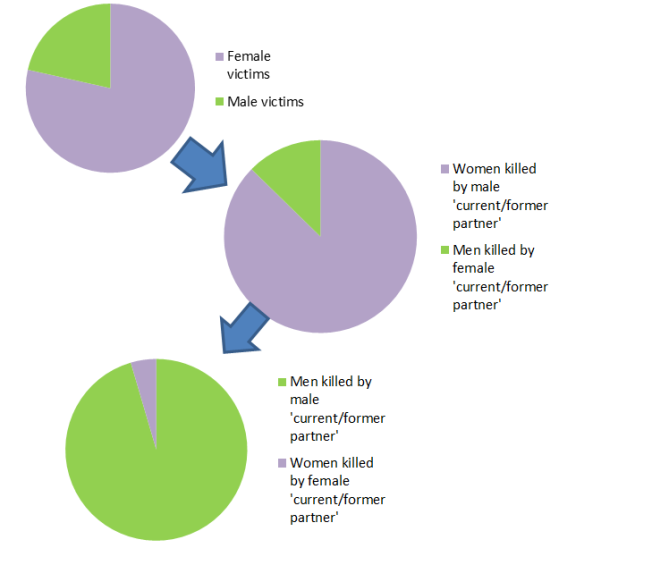
Combining data for the three years from 2011/12 to 2013/14, the ONS tell us that of 57 men killed in partner/ex-partner homicides, 21 of them, over a third, were killed by a man. Of these 21 men killed by men in the context of partner/ex-partner homicides, 14 of them were killed by a lover’s spouse/love rival. Of 249 women killed in partner/ex-partner homicides over the same 3 years, 247 were killed by a man, one by a woman (in one case the primary suspect is listed as unknown). None of the female victims of partner/ex-partner homicide were killed by the spouse of their lover or an emotional rival. Similarly, no male victims of partner/ex-partner homicide were killed by a female spouse of their lover or a female emotional rival. Not only are men killed in the context of an intimate relationship less likely to be killed by their actual partner or ex-partner, they are much more likely than women to be killed by someone of the same sex.
Another important difference between women and men killed in the context of intimate partner violence is the history of the relationship. When men kill women partners or ex-partners, this usually follows months or years of them abusing her, when women kill male partners or ex-partners, it is usually after months or years of having been abused by the man they have killed. (Browne et al., 1998; Websdale, 1999; Dugan et al., 2003.)
So, there are four important differences when we compare women and men killed in the context of a current or previous intimate partnership (figures from the ONS 2011/12 to 2013/14 data):
- Far fewer men than women are killed in the context of intimate partner violence (57 men in 3 years compared to 249 women)
- Men are much more likely to be killed by the spouse of a partner or a love rival (14 out of 57 men, compared to none of the 249 women killed)
- Men are much more likely than women to have been killed by someone of the same sex (21 of 57 male homicide victims were killed by a man, compared to one out or 249 women)
- Men are more likely to have been killed by someone they were abusing, women are more likely to have been killed by someone they were being abused by.
Finally, we could look at ‘domestic violence’ or violence between current and former partners rather than male violence against women and girls
The government has a ‘strategy to end violence against women and girls’, whilst this pitifully fails to name ‘male violence’ it does at least acknowledge that the issue is broader than domestic violence and it does indicate that women and girls are disproportionately victimised.
If we look at men who kill women (who are not current or ex- intimate partners), it is clear that they have more in common with men who kill female current or former partners, than the much smaller number of women who kill male former partners. When men kill women, regardless of their relationship or lack of it, they are doing so in the context of a society in which men’s violence against women is entrenched and systemic. Sexual violence runs through the murders of women by men who are not partners or ex-partners. Gender, the social constructs of masculinity and femininity are also integral.
What could we do if we wanted to hide the reality of men’s violence against women? We could ensure that our social and political agenda setters of mainly men – whose self-interest and privilege allowed them to consciously or unconsciously ignore, deny or dismiss the reality of men’s violence against women – not only hid the reality of men’s violence against women but also created the illusion that they’re dealing with the problem.